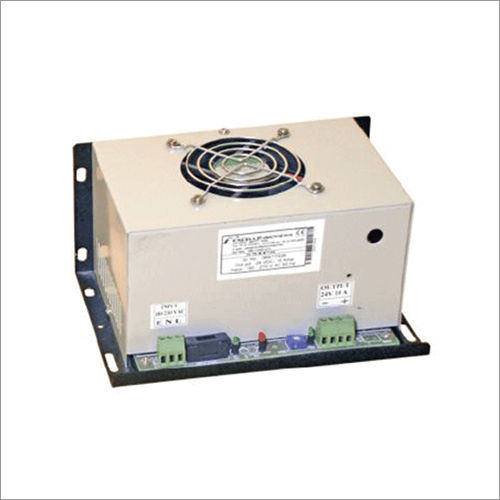
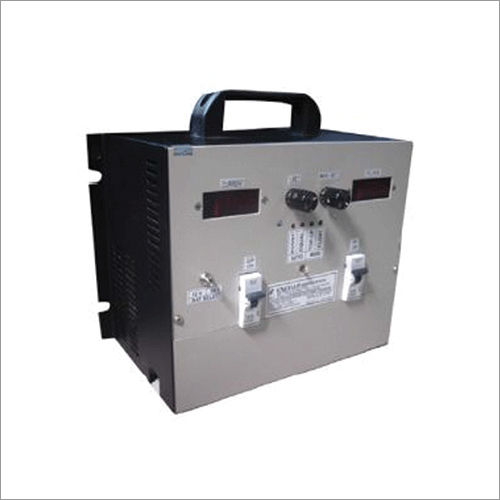
DC-DC Converter
Product Details:
- Application Industrial
- Product Type SMPS
- Material Mild Steel
- Click to View more
DC-DC Converter Price
- 5200 INR/Piece
- 1 Piece
DC-DC Converter Specification
- Mild Steel
- SMPS
- Industrial
DC-DC Converter Trade Information
- 5 Piece Per Day
- 1-7 Days
Product Description
A DC converter, otherwise called a voltage converter or voltage controller, is an electronic gadget or circuit that changes over one DC (direct current) voltage level to another, regularly determined to increment or diminishing the voltage. DC converters are usually utilized in different electronic applications to give steady and directed DC capacity to parts and circuits.
FAQs of DC-DC Converter:
Q: What is the essential capability of a DC converter?
A: The essential capability of a DC converter is to change over one DC voltage level to one more while keeping a steady and managed yield voltage. It can move forward (lift) or step down (buck) the information voltage to match the necessities of the heap or the application.
Q: How does a DC converter function?
A: DC converters work utilizing different techniques, including exchanging controllers and direct controllers. In an exchanging controller, the info voltage is turned here and there at a high recurrence, and afterward sifted and directed to create the ideal result voltage. In a straight controller, overabundance voltage is disseminated as intensity to keep up with the result voltage.
Q: How are DC converters chose for explicit applications?
A: The choice of a DC converter relies upon elements, for example, the expected information and result voltage levels, load current, productivity necessities, and size limitations. Planners additionally consider whether disengagement or guideline is required for the application.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry
