FHP AC Induction Motor Price
- 1 Piece
- 3075 INR/Piece
FHP AC Induction Motor Specification
- Black
- MS
FHP AC Induction Motor Trade Information
- 5 Piece Per Day
- 1-7 Days
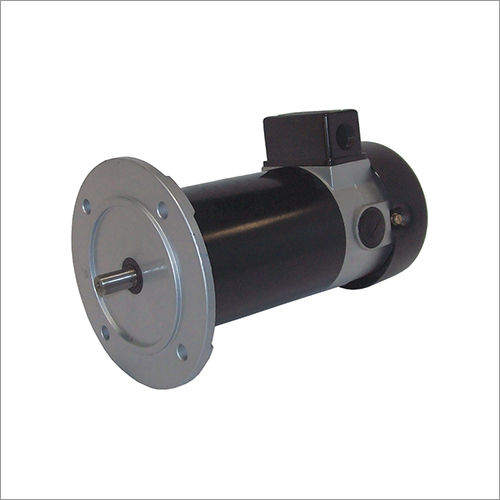
Product Description
A FHP (Fractional Torque) AC Induction Motor is a kind of substituting flow (AC) electric motor intended for applications where a somewhat low measure of mechanical power yield is required. These motors are regularly utilized in an extensive variety of little and medium-sized machinery, apparatuses, and hardware where the interest for power is under 1 pull (or 746 watts).
FAQs of FHP AC Induction Motor:
Q: What is the motivation behind a FHP AC Induction Motor?
A: The main role of a FHP AC Induction Motor is to change over electrical energy from an AC power source into mechanical movement or rotational power. These motors are utilized in different applications where little to direct measures of mechanical power are required.
Q: How does a FHP AC Induction Motor work?
A: FHP AC Induction Motors work on the rule of electromagnetic induction. They comprise of a stator (the fixed part) and a rotor (the turning part). At the point when AC voltage is applied to the stator windings, it creates a turning attractive field. This attractive field prompts flows in the rotor, making a force that makes the rotor turn and produce mechanical result.
Q: Are FHP AC Induction Motors reversible?
A: Indeed, numerous FHP AC Induction Motors are reversible by basically switching the course of the applied AC voltage. This turns around the pivot course of the motor.
Q: Could the speed of a FHP AC Induction at any point Motor be controlled?
A: The speed of a FHP AC Induction Motor is normally still up in the air by the recurrence of the AC power supply (e.g., 60 Hz in North America). Nonetheless, a few strategies can be utilized to control the speed of these motors, for example, utilizing variable recurrence drives (VFDs) or multi-speed winding game plans.
Q: How are FHP AC Induction Motors estimated or determined?
A: FHP AC Induction Motors are normally determined by their power rating in strength (HP) or watts (W), voltage, recurrence, speed, and actual aspects. The motor's size and determinations rely upon the particular necessities of the application wherein it will be utilized.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+




 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Call Me Free
Call Me Free
